
3DES FAQs
What is 3DES? Why is it used?
3DES cipher is a block symmetric cipher and is created based on the DES algorithm. It is also called Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA). Since it is a symmetric cipher, the same keys are used for encryption and decryption. 3DES is a symmetric key algorithm (translates to the the two parties communicating sharing the same keys for encryption and decryption) and can be used anywhere encryption is needed for example to secure communication between two parties or to encrypt file systems at rest.
What are some of the common applications of 3DES?
For several years, Triple DES was often used for electronic payments (for example, in EMV standard). New protocols based on the cipher are still being created and maintained (as for 2016). It was also used in several Microsoft products (for example, in Microsoft Outlook 2007, Microsoft OneNote, Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager 2012) for protecting user configuration and user data.
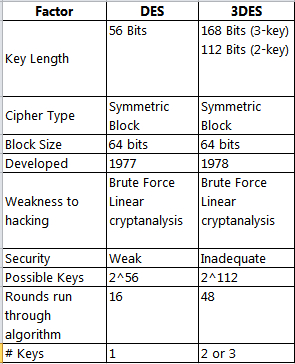
What is the difference between 3DES and DES?
 Is 3DES safe to use?
Is 3DES safe to use?
Yes. It is. But there are enough reasons to move on. Although there are no attacks that are practical to be carried out, you can expect 3DES to be phased out eventually. There are various reasons for this as mentioned here:
https://www.cryptomathic.com/news-events/blog/3des-is-officially-being-retired
Need help with a migration plan? Head over to our QuickStart section for more! To protect mission-critical data during the transition period to AES or another method of encryption, organizations can adopt stop-gap measures, such as changing 3DES keys more frequently.
What are "Modes of Operation" and why are they important?
Block ciphers should not be used as described in their original definitions. This is inherently weak since an adversary can build up a dictionary of different plain texts and their corresponding ciphertexts and use them to decipher an encrypted message. Besides the weakness in using encryption algorithms directly, there is also an added limitation where direct use cannot work on variable length of messages (the length of a message should be a multiple of the cipher block size in length).
The two popular modes of Operations are:
- Cipher Block Chaining (CBC)
- Counter (CTR)
Why are there different key sizes?
All the encryption algorithms can operate in different key sizes. A cipher is no stronger than its key length: if there are too few keys, an attacker can enumerate all possible keys. These different key sizes have different impacts on hardware/software and therefore an ideal sweet spot is choosing the right key length that offers enough security and provides good performance. Usually, the longer the key size the better the security but there are possible exceptions (for example, AES).
The length of each of the Block (broken chunks of data) is 64 bits and the available key length are 56, 112, or 168 bits.
What kind of attacks are possible on 3DES?
One of the major attacks that was possible on 3DES is called Sweet32. To read more about the attack, follow the link:https://www.synopsys.com/blogs/software-security/sweet32-retire-3des/
Ultimately, updating to the latest security protocols protects you, your users, and your reputation.
Advantages of using 3DES over other encryption algorithms? Is still one of the most widely deployed encryption algorithms. 3DES could be an intermediate upgrade from poor encryption algorithms like RC4. 3DES offers the best security among the other protocols in the DES family. Between DES and AES, there is no argument as AES is a clear winner.
Click here for understanding some of the high level differences between DES and AES:
For further reading: A comparison of the 3DES and AES encryption standards
How much overhead does it introduce in software and hardware? 3DES is very slow especially in software implementations because DES was designed for performance in hardware